- Details
- Hits: 2426
- Details
- Hits: 2434
The Aviators |
- Details
- Hits: 3030
| F/O Hugh Thornley Andrews | ||
|
|
||
|
b 28 Jul 1907, Swansea, Glamorgan RAF 1925-1930 He entered for the 1929 King's Cup Race, but withdrew before the start Chief Test Pilot for Spartan Aircraft Co Ltd, Woolston, Southampton, 1 Feb 1930 to 8 Sep 1931 He made two entries for the 1930 King's Cup Race, in Bluebird G-AATS and Spartan G-AAGO, and eventually flew in the latter but was unplaced. He then entered Spartan Arrow, G-AAWZ in the Europa Rundflug 3-week Air Race, 16 Jul-8 Aug 1930 Test Pilot for Fairey Aviation Co, Hamble, Nov 1931 to Dec 1933 RAF in WWII, then Sales Manager for Cunliffe-Owen Aircraft Ltd, 1946-52
Research: thanks to Steve Brew |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2452
| Flt-Lt John George Denholm Armour
|
- Details
- Hits: 4888
|
Flt Lt George Reginald Ashton
|
||
|
b. 14 April 1888, in Ryde, I.O.W. Began his career as a boy in the Royal Navy at the age of 15, and was transferred to the RAF via the naval wing of the RFC. Promoted to Flt Lt and posted to Iraq in 1924; in May 1928, posted to No. 1 School of Technical Training (Apprentices), Halton (hence his flying the H.A.C. II 'Minus' which, due to its tiny engine, got the most generous handicap of all the entrants in 1929) Got repeatedly transferred from place to place in the RAF (Armament and Gunnery School, Eastchurch in 1931; School of Photography in 1932; School of Naval Cooperation, Lee-on-Solent in 1934; 149 Sqn, Mildenhall in 1937). Sqn Ldr from April 1937, 2CFS at Brize Norton in 1938; awarded AFC in 1939. |
- Details
- Hits: 2262
| Harold John Vincent Ashworth, DFC | ||
 photo: 1928, aged 26 photo: 1928, aged 26 |
from Bournemouth. Died in WWII: 20th June 1942, when a Squadron Leader (pilot) with 218 Sqn, RAFVR; buried in Bergen, Holland. |
|
- Details
- Hits: 2984
|
F/O (later Flt-Lt) (Sir) Richard Llewellyn Roger Atcherley KBE, CB, AFC
|
||
|
Batchy', twin brother of David, b. 12 Jan 1904 1929 Schneider pilot and later Air Marshall in the RAF and Chief of Air Staff for the Pakistan Air Force. Put on a bit of weight later on, and ended up as Sales Director for Folland Aircraft. Died 18 Apr 1970. |
- Details
- Hits: 4598
|
Hon. Lady Mary Bailey Royal Aero Club Certificate No. 8067 (26 Jan 1927) |
|
 1927, aged 37 1927, aged 37 |
1930, aged 40 |
|
The Hon. Mary Westenra, b. 1 December 1890 in London but brought up mainly in County Monaghan, Ireland. Her family's home was Rossmore Castle, which was a grand affair built in the 1820s, with turrets, a vast drawing room and servants' quarters, not to mention about 20 cottages on the estate:
Here she is, with her brother Willie, and parents (Mittie and Derry) on a set of steps by the house, in 1913:
I visited County Monaghan in 2014 and asked in the local museum if they knew where the house was. 'Oh yes' they said, 'but it was demolished forty years ago'. It seems that it became severely infested with dry rot in the 1940s, was abandoned and, indeed, demolished in 1975. Anyway, here's all that's left of it now:
Mary married South African mining magnate and white suprematist politician Sir Abe Bailey in September 1911 (so, she was 21, he was nearly 47; his first wife had died in 1902 and he already had two children). They then had five more children - 2 boys and 3 girls. She learnt to fly at the London Aeroplane Club in 1926. She was the first woman to fly across the Irish Sea 'by the long route' from Chester to Dublin, the following August. The following March (1928) she began a solo tour to Cape Town, via Malta and then Cairo. Here, her plane was locked away by order of the Governor-General of the Sudan to prevent her from continuing alone, so she contacted Dick Bentley (who had flown to the Cape a few weeks before) to escort her in his own aeroplane over the "dangerous area of the southern Sudan". She then crashed in Tanganyika, writing off her aeroplane (she said it was her fault), but Abe made arrangements for a replacement Moth to be delivered from Pretoria and she continued, despite having 'flu. Abe was there to meet her when she arrived at the end of April. The return journey was made via the western 'French' route - the Belgian Congo, Angola and the French Congo. She finally arrived back at Croydon on 16 January, 1929, 10 months after she left. It was "undoubtedly one of the finest performances ever put up by a woman pilot." Lady Bailey was "so modest, so vague and so charming", and was "surprised that anyone should make a fuss about her journey". A Director of National Flying Services in 1929, (with Frederick Guest, Colonel the Master of Sempill, Alan Cobham, etc); she was also awarded the Brittania Trophy by the Royal Aero Club, and then made a Dame of the British Empire in 1930 for "services to aviation".
At the Chateau d'Ardennes in 1930
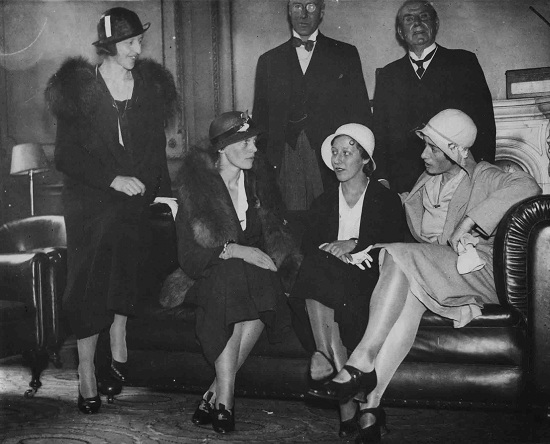

She was a guest at Amelia Earhart's reception at the Royal Aero Club in May 1932.
In early 1933 she gave everyone a scare by disappearing for several days on another solo flight to Cape Town; thankfully, she had only got lost, run low on fuel and landed safely in the Sahara. [Bert Hinkler, who disappeared at about the same time, was killed in the Alps]. She then flew back to England and almost immediately went down with a bout of typhoid, but recovered in time to compete in the King's Cup later in the year.
After that, she concentrated on looking after their horses, giving and attending loads more balls and receptions, and marrying off their many children. When Abe died in 1940, she settled near Cape Town (still keeping a house in Rutland) and died there 29th August 1960 aged 69.
Lady Mary's aeroplanes were: a 1926 DH.60 Moth (G-EBPU), a 1927 DH.60X Moth (G-EBSF, the one she crashed in Tanganyika), the replacement DH.60X Moth (G-EBTG, which Abe bought in Nairobi); a 1928 DH.60G Gipsy Moth (G-AABN); a 1929 DH.60G Gipsy Moth (G-AAEE) and a 1930 DH.80A Puss Moth, G-AAYA.
|
|
- Details
- Hits: 2592
| Mr William Richardson Bailey | ||
|
photo: 1920, aged 19 |
from Newport, Mon |
|
- Details
- Hits: 2526
|
Capt Harold Harrington Balfour PC MC
|
||
| b. 1 Nov 1897
Lord Balfour of Inchrye, Conservative M.P. for the Isle of Thanet in Kent. He used his DH Moth for electioneering in 1929, and was returned unopposed (i.e. nobody bothered to stand against him) with a majority of over 21,000 in 1931. In 1933 he published his autobiography, called 'An Airman Marches', in which he admitted that he had never paid some fines for driving offences in 1916 whe he was a trainee in the RFC; sure enough, Sussex Magistrates Court sent him a bill for the £3, plus 10 shillings costs, when they read the book. He sent them a cheque for £5. He (and Mrs Balfour, coincidentally) was back in a nursing home in 1934, this time for appendicitis. He became Parliamentary Under-Secretary for Air in 1938, helping to set up the Civil Air Guard, and flew a Spitfire in August 1938, saying that it was a 'very nice aeroplane for an old gentleman like me'. Once WWII broke out, he was a member of the Air Council, responsible for the Canadian part of the Empire Training Scheme, and flew a Whirlwind when he was 43 (although not in combat). After WWII, he was appointed 'Minister Resident in West Africa' by Churchill, but went to the House of Lords when that government was defeated. He was there until his death in 1988. |
- Details
- Hits: 2648
| Mr G E F Boyes | ||
|
|
|
|
- Details
- Hits: 6084
|
Capt Hubert Stanford Broad MBE AFC
|
||
|
b. 18 (or 20) May 1897 shot through the neck in WWI by one of Richtofen's Red Circus pilots; [c.f. Angus Irwin]; second in Schneider 1925, to Jimmy Doolittle. In 1928, he spent possibly the most boring 24 hours of his life by beating 'all existing figures' for long endurance flights in light aeroplanes (unfortunately there was no official 'record' to beat as such, the FAI not recognising such things). His log makes, um, rivetting reading: --0--0--0--0--0--0--0--0--0--0-- 5:30pm: Hendon 7:40pm: Gloucester 8:30pm: Coffee and sandwiches 11pm: Over Central London, 3,000ft; watched theatre crowds leaving Midnight to dawn: Remained over Edgeware 2:30am: second meal 4:10am: First signs of dawn 5:10am: Biggin Hill. Saw night bomber in air ... Noon: Stamford. Very sleepy 4:30pm: Ipswich --0--0--0--0--0--0--0--0--0--0-- Having trimmed the controls, Hubert settled down and read 3 complete novels 'to relieve the boredom'. When he finally landed, he he said that he was very stiff with cramp, and promptly went home to sleep. His Moth still had 12 gallons of fuel, so it could have kept going for another 4 1/2 hours... He was named as co-respondent in Beryl Markham's divorce in 1939. de Havillands test pilot until 1935 (Bob Waight succeeded him) - broke the world's speed and height records for light aircraft in the original monoplane Tiger Moth, then joined RAE Farnborough; Hawker test pilot post-WWII; died 1975 FLIGHT MARCH 28TH, 1946 No. 2. CAPT. H. S. BROAD, Senior Production Test Pilot, Hawker Aircraft Co. FOR sheer wealth of flying experience it is doubtful whether there is another pilot in the world to equal Hubert Broad. He has flown everything from diminutive single-seaters to multi-engined--bombers, and including a number of out-and-out racing aircraft. His logbooks, of which he has filled some nine or ten, total over7,500 hours' flying time and 182 separate types. These are honest types—not modifications or different mark numbers of the same aircraft. Many of these he has also flown as seaplanes. Broad, at the age of nineteen, learnt to fly at the Hall School of Flying at Hendon in 1915. The aircraft on which he made his first flight (there was no dual, a pupil did straights across the airfield until he felt it was safe to do a circuit)was the single-seater Caudron with35 h.p. Y-type Anzani engine. Believe it or not, with this tiny horsepower the Caudron occasionally was made to stagger into the air with two people on board, but the passenger had to sit on the wing by the side of the nacelle. Early Days The end of 1915 found Broad in the R.N.A.S. at Eastchurch, and he was on the very first course at Cranwell, which was then a R.N.A.S. establishment rejoicing in the name of H.M.S. Daedalus. His first tour of duty at the front was with No. 3 Squadron at Dunkirk. He was among a number of pilots lent by the R.N.A.S. to the R.F.C. No. 3 Squadron flew Sopwith Pups, and it was while he was on one of these, escorting a bombing raid by 90 h.p. R.A.F.-engined B.E.s, that he was shot through the neck by one of Richtofen's later Goering's—Red Circus pilots. On recovery he spent a while as an instructor at Chingford and then went for his second tour of operations with No. 46 Squadron, who flew Sopwith Camels. The end of the 1914-18 war found Broad instructing at the Fighter Pilots' Flying School at Fairlop. Peace found him, as it found so many other young fellows ,with the ability to fly aircraft superbly and no other means of making a living. But a good living could be made by joy-riding in the early 1920's. First he joined the Avro Company, who were running joy-riding in a fairly big way, and in 1920 went to the Adiron Lakes in America with two Avro 504 seaplanes. These two aircraft saw their last days in Long Island, where they were completely wrecked by an autumn gale. By the next year he was back in England competing in the Aerial Derby air race round London on a Sopwith Camel. He finished 6th.In October, 1921, Broad joined de Havillands. Those who know this great concern now will smile to learn that when it started in those days it consisted entirely of two fabric hangars and a hut at Stag Lane. If memory serves, the capital of the company at that time was £100. The D.H. series numbers, which started in the Aircraft Manufacturing Co. Ltd., were carried on in this new firm, and Broad flew every one of the D.H. designs from the D.H.27 to the D.H.90. In the same period he did a lot of test flyingfor other aircraft constructors. He did the W.10, Handcross, Hendon, and some others for Handley Pages, the Parnall Pipit and the Saunders A. 10 fighter. On the Gloster Grebe he ran into wing flutter for the first time (this trouble, in those days, was on a par with the compressibility troubles we have now). Seaplane testing Another big job he did was most of the development work on the Gloster II and III racing seaplanes. Over a period I used to go with him to Felixstowe regularly. As a Press man I was forbidden the precincts of the R.A.F. seaplane station, but there was a perfectly good Great Eastern Railway pier alongside the station. I used to climb over the fence and watch the proceedings from the pier head. Broad nearly lost his life there one day in October,1924. As he was landing the Gloster II a forward strut to the floats collapsed, and the aircraft turned completely over. Mrs. Broad was watching from the shore, and it seemed a very long time before Hubert appeared on the surface. In 1925 Hubert Broad flew the Gloster III racing seaplane in the Schneider Trophy contest which was held that year over Chesapeake Bay in America. This was the race in which Henri Biard, flying the SupermarineS.4—the true forerunner of the Spitfire—crashed in the water with wing flutter. Broad finished this race second to Jimmy (now General) Doolittle. That must have been a vintage generation, because many names from that period have found their way into the high-spots of this last war. With the advent of the D.H. Moth in all its variants, Broad was to be seen performing aerobatics at most flying club meetings and entering many of the races. These included the King's Cup Race, which he won in 1926. He was flying a delightful Cirrus I Moth, which was a study in ivory and red. His average speed over the whole732 miles was 90.4 m.p.h. His piece de resistance in aerobatics was a perfectly formed big loop, the base of which was only some 150ft from the ground. It was a joy to behold, but very dangerous to perform. Broad had sufficient sense to realise this and sufficient courage to stop doing it. "Hooked" It was during an aerobatic show that Hubert had his closest shave in a life packed with incident. And it was so simple. Flying a D.H. Tiger Moth with no one in the front seat, he did a slow roll—a stunt at which he was a master. The safety belt in the empty cockpit was loosely done up. While the Moth was inverted the belt hung down and, as the aircraft turned the right way up again, the belt came back over the joy-stick. The result was that Broad had only about 1 1/2 inches of stick movement; but, nothing daunted, he made a sort of tail-up, seaplane landing. In this connection it is to be remembered that there were no lovely 2,000-yard runways on which to this sort of thing. In those days there was not a single runway available in Britain; not even for the take-off of over-loaded aircraft for long-distance records! Another unhappy moment occurred when he found the tail trim (the incidence of the whole tailplane was adjustable)of a D.H.34 had been connected in reverse. By a good deal of jockeying he managed to get into Northolt. On yet another occasion a careless mechanic left a screwdriver jammed in the chain and sprocket of the rudder actuating gear. This necessitated a down-wind, crosswind, finishing up into-wind landing at Hendon airfield, because that was a bit bigger than Stag Lane. One of the prettiest little aircraft he ever flew was the original D.H. Tiger Moth monoplane. This was tailored exactly to fit Broad. Physically he is not of big stature and few other pilots could get into the machine. In the front of the cockpit was a bulkhead which had two holes just large, enough for the feet to be threaded through, and these holes had to be padded with sorbo rubber so that Broad's shins did not get barked while landing and taxying. Springing was almost non-existent. Span was22ft 6in and length only 18ft 7m. In August, 1927, on this machine he broke the world's record for light aircraft for both speed and height. For the former the figure was 186.47 m.p.h., he having taken19 min 59 sec to cover the 10 km, and for altitude he reached 20,000ft in just 17 min. A year later he took two more world's records on the D.H. Hound. In 1935, after 20 wonderful years of service, he left de Havillands and later did some flying for the Air Registration Board. From here he went to the Royal Aircraft Establishment and finally joined Hawkers to be in charge of all their production testing at Langley. He will be 50 in a matter of a few weeks, yet every day sees him at oxygen height testing Tempest IIs. As he says, he has gone from 35 h.p. in the Anzani to over 3,000 h.p. in the Centaurus and Sabre VI, and from 2 ½ lb/sq ft in the Caudron to 40 lb/sq ft in the Tempest II. |
- Details
- Hits: 2343
|
Flt-Lt T B Bruce
photo: 1930 |
- Details
- Hits: 2556
|
Mr Maurice Brunton
b. 6 Sep 1906, Preston, Lanc RAF 1925-38; Pilot for Imperial Airways, 1939
d , 21 Nov 1971 - London
Research: thanks to Steve Brew |
- Details
- Hits: 2922
| Mr Alan Samuel Butler J.P. | |
|
photo: 1921, aged 23 |
Chairman of de Havilland; the story goes that in 1921 he asked the one-year old de Havilland Aircraft Company to build a fast two-passenger touring aeroplane to his specification, and stumped up £3,000 for them to do it. The money saved the company from extinction and they appointed him to the board of directors forthwith. He held the position until he retired in 1950. The aeroplane became the DH37, (which he named, firstly, 'Sylvia' after his sister, then, rather diplomatically, 'Lois', after his wife, q.v.), which he entered in the very first King's Cup Race in 1922 and again in 1924, coming third. He and Lois set up a world speed record of 120mph for 1000 km in 1928, and they also flew to Cape Town together . Entered the MacRobertson Race in 1934 (assigned No 59) but didn't take part. Was still aviating in 1970. |
- Details
- Hits: 2741
|
Mrs Lois Butler Royal Aero Club Certificate 8634 (14 Jun 1929)
|
|
Née Reid b. 3 Nov 1897 in Montreal, Canada; the "beautiful" [so said Harald Penrose] wife of Alan Butler. (later, the 'Flying Grandmother', oh well...) Her first husband having died in 1923, she married Alan Butler in 1925; together they had a daughter and a son. 15th in the Women’s Combined Alpine Skiing at the 1936 Winter Olympics, skating for her native Canada (although she was a member of the British Team before that).
Post-WWII, the Butlers moved to Rhodesia and bought a tobacco farm, but eventually moved back to Studham Hall, Bedfordshire. She owned a 1930 DH.80A Puss Moth G-ABGX, which was sold in France in December 1934, re-registered as F-AMRX and whose registration was finally cancelled in 1936.
d. 17 Aug 1970 in Piraeus, Attiki, Greece from a heart attack while on holiday, and is buried in Studham. |
- Details
- Hits: 2525
Capt Robert George Cazalet
|
|||||
- Details
- Hits: 2439
|
Mr John William Pender Chalmers
photo: 1928, aged 40 |
||
| born in Morro Velho, Brazil |
- Details
- Hits: 2356
|
Capt (later Sir) Geoffrey de Havilland O.M. K.B.E A.F.C Hon.F.R.Ae.S |
||
| Geoffrey de Havilland - Wikipedia has his story |
- Details
- Hits: 2529
| Mr Vincent Neville Dickinson | ||
|
|
||
|
Father: Frank Dickinson, a Merchant, Mother: Sarah Jane [Bayley] 2nd-Lieut, RFC, RAF in WW1; Pilot Officer from 20 Nov 1923 He was one of two pilots who inaugurated the Belfast to Liverpool Daily Air Service in April 1924 (the other was Alan Cobham), He started out at 05:30am in his D.H. 50, but the weather was so bad he could get no further than Southport Sands. m. 18 Nov 1923 in Richmond-upon-Thames, Marjorie Winifred [Lloyd-Still] (1 daughter, Katheen b. 1926) Elected a Member of the Royal Aero Club in June 1925 Formed Aero Hire Ltd in 1927, based in Birmingham, to "establish, maintain and work lines of aeroplanes, seaplanes and taxi-planes and aerial conveyances, etc. (later co-owned, with L W van Oppen,) Competed in the King's Cup in 1929, flying G-EBTH, a DH.60X Moth. He was forced to retire at Blackpool. Hon. Secretary and Chief Instructor, Hertfordshire Flying Club, St Albans in 1932
He owned G-EBZZ, a 1928 DH60 X Moth, which crashed at Stansted Abbots 23 Jun 1934
One reported accident: - 14 Mar 1939, flying G-AEDD, a 1936 Avro 504N belonging to Publicity Planes Ltd; he hit a fence and crashed at Calderfields Farm, Walsall, after engine failure. Address in 1939: 'Muree', Queen's Rd, Sandown, Isle of Wight
Briefly (5 Jun to 5 Jul 1940) a pilot for the Air Transport Auxiliary (ATA) Sub-Lieut in the Royal Navy from 15 Jul 1940 Address in 1962: 10 Oakwood Rd, Rayleigh, Essex d. 3 Sep 192 - London |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2340
| Flt-Lt (Sir) Edward Hedley Fielden KCVO CB DFC AFC | ||
|
|
||
|
'Mouse', b. 1903. Prince of Wales' (i.e. Edward VII's) pilot, later Captain of the King's (and Queen's) Flights until 1962. DFC, 1943: "This officer has flown on various operational missions, some of a most hazardous nature. He has displayed a high standard of operational efficiency, setting an example which has contributed materially to the high morale of the air crews under his command. His great organising ability has proved a valuable asset.” Edward Fielden (RAF officer) - Wikipedia d. 1976 |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2539
|
William Forbes-Sempill, 19th Lord Sempill AFC |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Ah... yes... the aviation pioneer, chairman of the Royal Aeronautical Society, right-wing sympathiser and occasional spy (for the Japanese), who was motivated by his 'impetuous character, obstinacy, and flawed judgement', rather than money. |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2215
| Mr Phillips Patrick Grey | ||
|
|
|
|
|
b. 1 Jul 1903, Bakewell, Matlock, Derbys, RAF 1924-29 Flying Instructor, de Havilland, Stag Lane, 1929 RAF, 1940-45 d. 29 Apr 1989 - Hindhead, Surrey
Research: thanks to Steve Brew |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2688
| Capt Walter Laurence 'Wally' Hope | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Technical director of Air Freight. b. 9 Nov 1897 in Walton, Liverpool Aged 18, and described as a "trick-cyclist", he was summoned in 1915 for committing a breach of the Realms Act by taking a photograph of one of his Majesty's ships at Barrow; he pleaded not guilty, admitted that he was carrying a camera, and was fined £5. A close friend of Bert Hinkler, he made an extensive search over the Alps at his own expense when Bert went missing on his fatal flight in 1934, but then sued the Daily Mirror when they published their hair-raising account of his exploits, "Captain Hope's Ordeal in the Alps". He said there was "not one word of truth in it." m. 1920 Marjory [Stone] Three-time winner of the King's Cup Race (1927, 1928 and 1932) In the 1926 King's Cup race, "he had to descend at Oxford while racing for home in the last lap with a small “airlock" in his petrol pipe, which effectually put his tiny Moth machine out of the running. He landed in a small field - so small that he found it impossible take off again when his minor trouble had been rectified without pushing his plane through three fields to a broader stretch of country, where he could rise. By this time it was so late that he decided that would abandon the race and go on at his leisure to Hendon. Interviewed at his home in Hendon yesterday, Mr. Hope said: “The only thing that I am really disappointed about is that I feel sure that if this trifling mishap had not occurred I should most certainly have won. For three laps I was racing neck and neck with Captain Broad, with an aggregate speed equal to his - between 90 and 91 m.p.h." Daily Herald At the end of the 1928 race, "Thinking all was over he proceeded to loop and stunt before landing, and having landed switched on his well known winning smile. Suddenly there was a terrific hooting, and Sir Francis McClean in his white Rolls-Royce came tearing across to tell Hope he had not crossed the finishing line... Within 30 seconds Hope was in the air again, discovered the finishing line, landed, and again switched on the winning smile fortissimo." C G Grey Entered for the MacRobertson Race in 1934 (No 24) but didn't take part in the end. m. 1954 Hilda L [Stone or Hunt] d. Oct 1979 - Isle of Wight |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2460
| Mr John Duckworth Irving | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Born in Xlanga, S Africa but living in Northumberland; 'a shopkeeper' |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2447
| Mr Alfred Charles Morris Jackaman | ||
|
|
|
|
|
A civil engineer from Slough; in 1936 he and Marcel Desoutter decided that an airport at Gatwick might be a nice idea (it was, after all, "outside the London fog area"). He later married Australian-born Muriel Nora 'Cherry' Davies and they ended up near Sydney; he died in 1980, but she survived until 2011 - aged 101. see |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2164
| F/O R W Jackson | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Later a Wing-Commander; Wing Commander R. W. Jackson (R.A.F.), Albert Street, Castleton. January, 1945. New Year's Honours List 1945. Twice mentioned in despatches, and given the Air Efficiency Award in 1944. "TECHNICAL BRANCH. Promotion. Notification cancelled. 13th Sept. 1949 '(p. 4395, col. 2) concerning R. W. JACKSON, O.B.E., A.M.I.Mech.E., A.iR.Ae.S.(70343)." |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2202
| Flt-Lt A M Kimmins | ||
|
|
|
|
| ?? | ||
- Details
- Hits: 2498
| Mr Harrington Robley Law | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Originally from Scotland; son of Bonar Law. In 1939 a member of the Insurance Flying Club. Apparently he had a lisp, but was very able. |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2745
| P/O (later F/O, Flt Lt) Haliburton Hume Leech | ||||
|
photo: 1926, aged 18 |
|
|||
|
Haliburton H Leech was born 16 Apr 1908, in Wylam-on-Tyne, Northumberland. He competed in 6 King’s Cup races – every year from 1929 to 1934. His father, Dr. (later Sir) Joseph William Leech, J. P., was the Sheriff of Newcastle-upon-Tyne, and later its M.P.; at the time they lived in Wylam Hall, which according to English Heritage is a vast “rambling house built in the 15th century with 18th-19th century alterations, since divided into 3 apartments”. Haliburton was the youngest of 3 sons. He went to Harrow from 1922 to 1925, then gained his Royal Aero Club Certificate (No 7993) at Cramlington with the Newcastle-on-Tyne Aero Club, flying a D.H. Moth, on the 10 Apr 1926.
In 1931, Flight described him thus: “… a well-known figure at flying meetings, as his aerobatic demonstrations in the Martlet are always amongst the prettiest to be seen. He entered Cranwell as a cadet in 1925, finally leaving there and being posted to Tangmere in 1927. He was promoted to Flying Officer in July 1929, and in 1930 went to the Royal Aircraft Establishment at Farnborough, and has since been engaged on a great deal of test work, flying a large variety of machines. This year he was selected as one of the members to join the High Speed Flight at Felixstowe preparatory to receiving his training to take part in the forthcoming Schneider Trophy Race, but, much to his disappointment, he was later sent back to Farnborough, as it was found that there were too many pilots in the flight. F/O. Leech has raced on numerous occasions in light aircraft, and is always consistent.” However, during one such aerobatic demonstration, one cynic pointed out that "After all it does not matter if he does crash, as his father is a doctor!” In 1932, he piloted the Royal Aircraft Establishment’s Scarab (a parasol-wing modification of the D.H. 53 Humming Bird) on its first flight.He was posted to the School of Naval Co-operation, Lee-on-the-Solent, on the 1st March 1934, then (as a Flight Lieutentant) to No. 824 (F.S.R.) Squadron, Upavon, on the 8th October 1934.
He was best man at his elder brother Basil's wedding to Grace Luckham in September 1937, then married Miss Ruth Janet Chernocke Elliott (the younger daughter of Mr and Mrs A E Elliott of Little Hill, Bromeswell, Woodbridge) at Eyke Church, Suffolk on 9th October 1937. The happy couple then left by air, from Martlesham, 'for abroad'. He retired from the RAF in September 1938 due to ill-health, and died 5th May 1939, in St Bartholomews Hospital, when he was only 31. Unusually, 'Flight Magazine', who carried innumerable references to his flying displays, carried no news of his death - normally they would have produced a short obituary of someone so well-known in aviation circles. His gravestone (with thanks to the Gravestone Photographic Resource) is in Eyke Church:
His father, Sir Joseph, died a year later. Ruth married a Mr Foster in 1940 and died in 1986 in Ipswich; she was referred to as 'Ruth Janet C Lady Foster'. He competed in loads of air pageants and races throughout the 30s, including: - The Kingston-upon-Hull Air Race, at the Hull Air Pageant which was held to celebrate the opening of the Hull Aero Club clubhouse in April 1930. The 7 entrants were Leech (flying "Miss Perry's D.H. Moth G-AASG" *); Winnie Brown flying her Avian G-EBVZ; Winifred Spooner in her D.H. Moth G-AALK; Ivor Thompson (D.H. Moth G-AACL); Alfred Jackaman (D.H. Moth G-AADX); Robert Cazalet in his Westland Widgeon G-EBRM, and Capt G Thorne in Avro Avian G-AAHJ. Leech finished first but was disqualified for ‘not turning at one of the marks’.
* Miss Violet Perry (seen here), who flew at the Berks Bucks and Oxon Club, is not listed as the owner of G-AASG, though; it apparently belonged to 'Miss M Shillington'. September 25, 1932 saw him coming 3rd in the Yorkshire Trophy Race - "175 and a half miles over two triangular circuits" in the Arrow Active, behind Edgar Percival in a Gull, and Col. Louis Arbon Strange in his Spartan. Later, "F/O. Leech gave one of his thrilling, if not hair-raising, displays on the Arrow Active."
A few weeks later (12 August 1933), he put up the fastest time in the London to Newcastle Race in Richard Shuttleworth's Gypsy-engined Comper Swift G-ABWW, but ended up 5th (of 10) on handicap. He received a cheque for £10 for his effort; the 166.09 mph was "the highest registered speed obtained on any British light aircraft" at the time. In July 1937, he was listed as one of 15 competitors in the Devon Air Race (which also included Alex Henshaw, Connie Leathart, Tommy Rose and Geoffrey de Havilland) but withdrew before the start. In the King’s Cup: 1 - G-EAUM (1929) This aircraft was a real-old-timer, an Avro 534 ‘Baby’, first registered in July 1920. Squadron Leader Harold Payn had raced it in 1922, and R. A. Whitehead (who sold it to Leech) in 1928. Leech, in turn, sold the aircraft to H.R.A. Edwards, and it was finally withdrawn from use in November 1934. 2 - G-AALK (1930) This D.H.60G Gipsy Moth was almost new (first registered August 1929), and belonged to the Household Brigade Flying Club at Hanworth. It was flown by Squadron Leader the Hon. Frederick E Guest in the 1931 race, then went to Wrightson Air Hire, but crashed at Shackend Railway Station near Hawick in April 1937. 3 - G-ABIF (1931) This Southern Martlet 205 had only been registered in January 1931, and belonged to Miss J Forbes-Robinson. Theodore C Sanders flew it in the 1933 King’s Cup race. It was withdrawn from use in 1940, but went to the ATC during WWII, until it was finally cancelled in December 1945. 4 - G-ABVE (1932, 1933) G-ABVE was the only Arrow Active II ever built, registered in March 1932 to Arrow Aircraft Ltd of Yeading, Leeds. Leech flew this aircraft in the 1932 and 1933 races, achieving 137mph. In an extraordinary link with MacRobertson aviator Geoffrey Shaw, they were together in July, 1932: "Six members joined the Yorkshire Aeroplane Club during June, amongst them being Mr. Geoffrey Shaw and Mr. A. C. Thornton. The latter is the designer of the" Arrow Active," and his latest production, the "Active II" has been much in evidence, being tested by F/O.H. H. Leech." After the race, it was stored at Yeading until 1957 before being completely renovated in 1958, with the installation of a 145-hp Gipsy Major engine. It survives, and is now in the Real Aeroplane Collection at Breighton Aerodrome, Selby, Yorks. 5 - G-ACUP (1934) Unfortunately, the registration of this brand-new Percival D.3 ‘Gull Six’ did not prove prophetic; Leech only managed fifth in the heats, despite averaging 160mph. The Gull went on to re-appear in the Kings’ Cup in 1938, flown by H Thomas-Ferrand, and was then sold in Australia in May 1939.
|
||||
- Details
- Hits: 2311
| Mr Edye Rolleston Manning | ||
|
|
|
|
|
Later Air Commodore; died 1957 |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2388
| Mr Carill Stanley Napier | ||
|
|
|
|
|
b. 29 Apr 1907 From Putney, London Son of the famous engine-maker Montague; an apprentice with Westlands in 1929. 'his one recreation apart from flying is the commendable indoor sport of darts. Believes that air-racing is good fun only when taken not too seriously'' Killed in WWII: 29 April 1941, when a First Officer in the Air Transport Auxiliary; buried RAF Halton, Bucks. see https://www.ata-ferry-pilots.org/index.php/category-blog-1939/53-napier-carill |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2680
| Wing-Cmdr Harold Melsome Probyn | ||
|
|
|
|
|
from Lancashire, later an Air Commodore; retired to Kenya. Felt that aviation wasn't as much fun after the invention of the parachute. In 1927-8 he entered as 'Harold Brooklyn', and 1929-31 he entered as 'J Wellworth'; I have no idea why. |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2300
| Lieut Llewellyn George Richardson, RN | ||
|
photo: 1930 |
|
|
|
Royal Navy 1922-1951, but RAF 1925-36 |
||
- Details
- Hits: 3061
| Flt-Lt Thomas 'Tommy' Rose DFC | ||
|
|
|
|
|
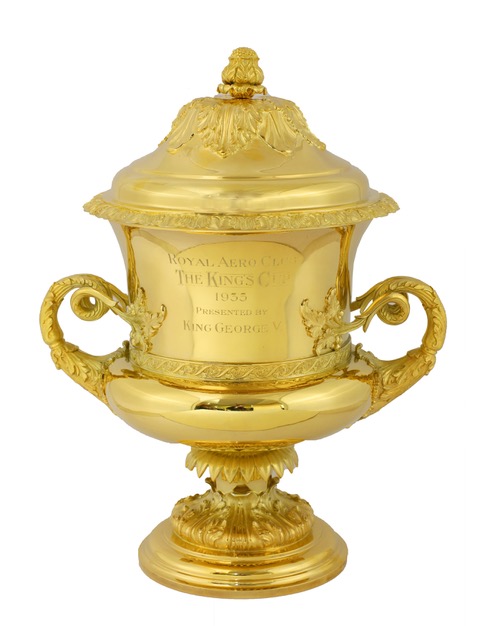
b. 27 Jan 1895 - Alton, Hants One of the best-known racing and pioneering pilots of the 30s. His father, John, was a farm bailiff at Basing Farm, Froxfield, nr Petersfield, Hants. After working briefly as a bank clerk, Tommy joined the Royal Navy in 1914 and then transferred to the R.F.C. in June 1917. "He was shot down three times, but escaped each time. He was awarded the DFC for his work with the fighter squadron in which Billy Bishop, VC, served. " m. 1925 Margaret Elizabeth [Ashford], [divorced 1938] Retired from the RAF in 1926 with the rank of Flight-Lieutenant. In December 1931, he made an unsuccessful attempt on the UK-Cape record, and then flew back "by easy stages". From Oct 1933, Manager and Chief Instructor at Sywell. "TOMMY ROSE is gone from Sywell, but not forgotten. As sales manager for Messrs. Phillips and Powis, the Reading aircraft manufacturers, he spends quite a lot of time flying round the country. Last week his photograph was 'splashed' in all the national daily papers, greeting Mr. H. L. Brook, the Yorkshireman airman, on his arrival at Croydon after breaking the Australia-England record previously held by Jim Mollison. There was no mistaking Tommy’s famous sports jacket and boyish grin! Mr. Rose, the way, left a last impression at Sywell. Shortly before leaving, when the new gate was being erected in front of the clubhouse, he carefully placed his foot in the wet cement and printed beside it 'Tom Rose' with a trowel. The cement hardened, and the 'Rose' mark is there for posterity to reverence! Hundreds of feet have since trod the hallowed spot." - Northampton Mercury, 12 April 1935 Competed in the King's Cup six times, winning it in 1935 ...
© The Royal Aero Club [0122-0170] ... and coming second in 1934 and 1936. [The 1935 King's Cup itself recently sold at auction for £3,900:
Photo kindly supplied by Sarah Chambers, reproduced by kind permission of Sworders Fine Art Auctioneers.] He became a national hero in March 1936 after his flight to Cape Town and back; "he can now claim to have made the fastest time for the trip both out and home. His new record is 6 days 6 hr. 57 min. (he got to the Cape in 89 hr. 37 min.), which beats F/O David Llewellyn's time—the previous best—by 5 hr. 6 min."
After the flight to the Cape, he had tea with the Prime Minister, General Hcrtzog, and also saw General Smuts. However, he was charmingly modest about his achievements: "TOMMY ROSE ON LONG FLIGHTS SAYS RECORD ATTEMPTS ARE 'LARGELY BUNKUM' This flight business is bunkum! The authority for that picturesquely phrased piece of information is Flight- Lieutenant Tommy Rose, and he should know, for he hit the headlines in all the national newspapers when he smashed all records for the flight from London to the Cape. In a talk to the Round Table at Stewart's Cafe on Monday he summed up the whole business in these few words: 'All long distance flights are largely bunkum. The national newspapers, if there is no other news at the time, whip up an interest in these flights, and if one gets there safely and breaks a record everyone thinks: 'By gad, here's one of the twelve apostles come to life!’ (Laughter.) 'But I assure you there is nothing in it. The only things you have got do to be successful are to get the best machine you can find and then practise sitting still for a long, long time . . . . ' Reflections wise and witty on flying in general and his own flight in particular made Flight-Lieutenant Rose's talk one of the most delightful and amusing to which Tablers have listened to for a long time. His racy manner produced a laugh at almost every sentence, and a more unassuming world record breaker than this genial young man would be difficult to find. There was one richly humorous story which is worth repeating. 'When I eventually got to the Cape I had to broadcast to the Union,' he said. 'The announcer seemed very nervous and this was what he said: ’Who do you think I have here the studio? None other than Mr Tom Mollison, who flew from London to the Cape in 37 days 18 hours.’ I met General Hertzog few days later and he said: 'if it takes all that time to fly, don't you think you had better come by boat next time?’ Flight-Lieutenant Rose answered a number of questions and urged the need for municipalities laying down landing grounds for aircraft. Members of the Rotary Club and of other Round Tables were present, as guests, to hear the airman’s talk. " - Eastbourne Gazette, 6 May 1936
© The Royal Aero Club [0129-0039] Before the 1936 Schlesinger Race to Johannesburg, he predicted: "It is my opinion that the pilot of the aeroplane which gets there in under forty-eight hours will deserve just about the biggest bunch of bananas ever found. Having got lost myself many times down this route when flying without wireless, I fully expect to do so again, and the pilot in this race who can honestly say at the end that he was sure of his position all the time will either be very lucky, very clever, or have a queer idea of honesty." From 1939 to 1946, Chief Test Pilot for Miles Aircraft, living in Sonning, Berks; in July 1943 he was reported to have "improved considerably and to be well on the way to recovery, after he contracted a chill when captaining his works cricket team. " Won the Manx Air Derby in 1947, still flying a Miles Hawk; three circuits of the island at 181 mph. d. 20 Jun 1968 - Alderney, Channel Islands. |
||
- Details
- Hits: 3192
|
Miss Winifred Evelyn Spooner Royal Aero Club Certificate No. 8137 (11 Aug 1927) |
|
 1927, aged 27 1927, aged 27 |
 |
|
'Bad luck Wimpey' was one of the best-known women aviators of the time, and the one generally regarded as the best. She was awarded the International League of Aviation's Trophy for women aviators in 1929, and in 1930 Capt C D Barnard described her as 'the finest woman pilot in the world' (He went on to say that Lady Bailey was regarded as the 'second finest airwoman in the world', and we don't know what she thought about that...) Learnt to fly in 1926 and took it 'more seriously than most' - in her first race in April 1928, she won the Suffolk Handicap (21 miles at 78mph), ahead of Neville Stack and four other male rivals; she won the 'heavy' category in the Round Europe Contest for Touring Aircraft in 1930 - covering 4,700 miles at 102mph, ("a very fine performance indeed", said The Times) and also competed in the Ladies event at Reading (May, 1931) - the other competitors were Amy Johnson, Grace Aitken, Pauline Gower, Dorothy Spicer, Susan Slade, Gabrielle Burr, Christina Young, and Fidelia Crossley - a historic gathering indeed. Photo here
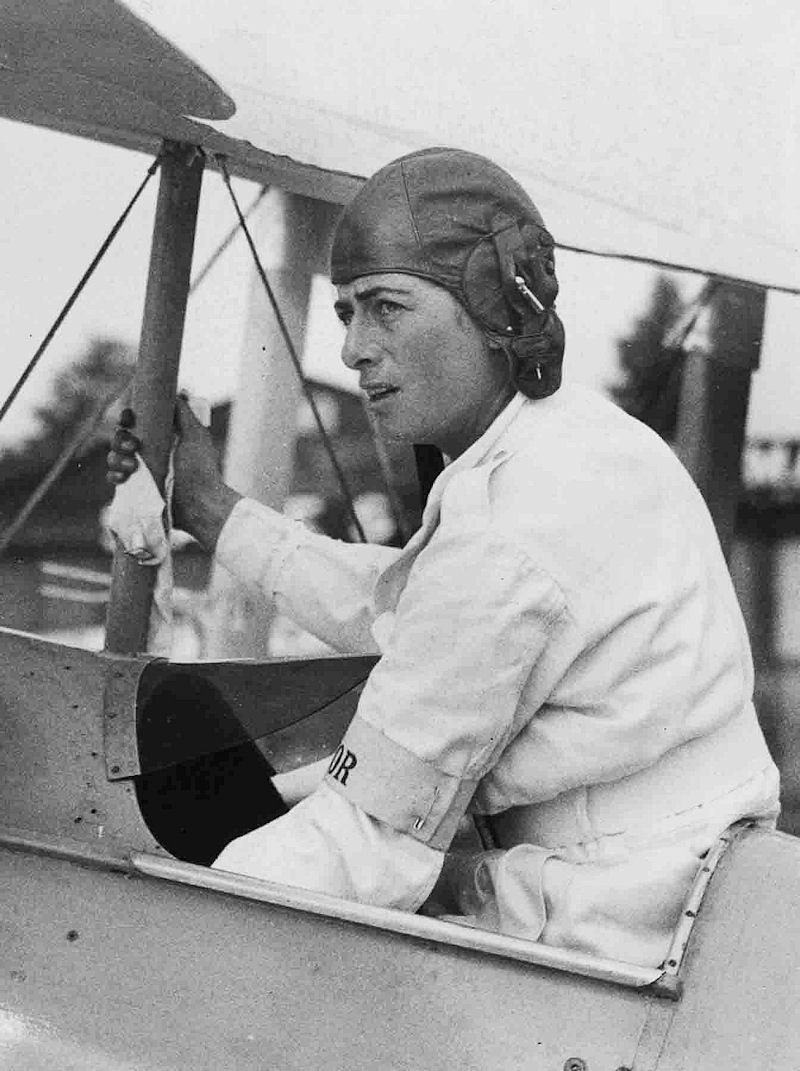
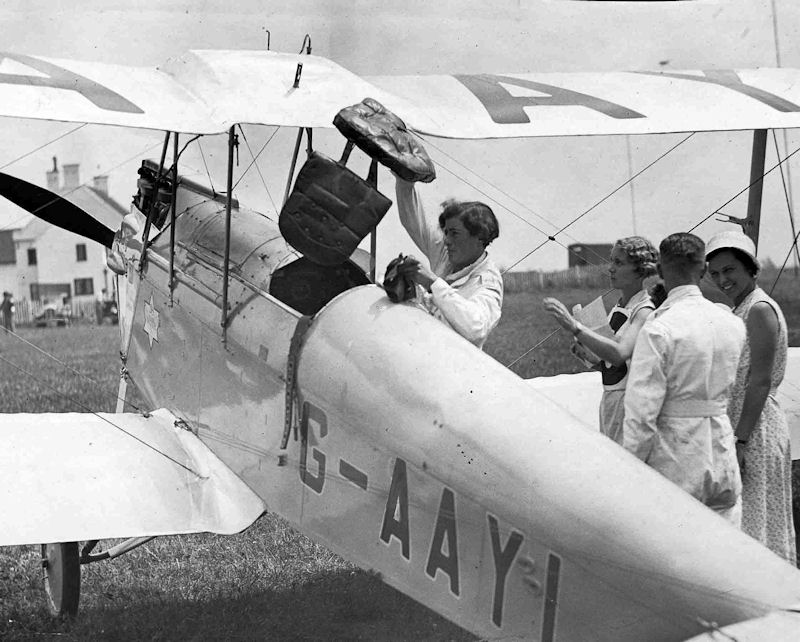
She soon took her 'B' (Commercial) Licence, and at one stage was the only professional woman pilot in the country. In September 1927 her first flight abroad was to Venice to support the British Team in the Schneider Cup in Venice. Alan Butler (with Peter Hoare as passenger), and Hubert Broad, who took Maia Carberry, also went and, in case you were wondering, "Mrs. Carberry wore a pale blue leather flying helmet to match the colour of her Moth aeroplane." She soon became regarded as 'one of the few women who matter in the air world'; in March 1928, when King Amanullah of Afghanistan was on a state visit to London, he inspected "the latest types of Imperial Airways passenger machines and a number of small Moth machines in private ownership. He carried on, through an interpreter, an animated conversation with Miss Winifred Brown, of Manchester, and Miss Spooner, of London, both of whom own and fly small two-seater machines." In the 'Woman's World' section of the Inverness Courier of April 1928, this description of Winifred appeared: "[she] has not flown for very long, for it was only about three years ago that I knew her in Cologne, when she then drove, instead of an aeroplane, a two-seater car, through the crowded streets of Cologne, at a speed which most people would have been terrified to attempt. She was always, however, extremely cool and composed, and though her passengers were sometimes nervous she never seemed so. She was always very sporting, and played an excellent game of tennis. A good-looking, typically English girl, she made many friends among the British army in Cologne when doing voluntary work with the Y.M.C.A. there. [Winifred was with the 'Army of Occupation' in Germany at the time]" She did have what she later described as her 'greatest air thrill' on Marlborough Common in May 1929; "she had been taking passengers up all day when, after one flight, she said she was not quite satisfied with the controls, and refused to take the next man until she had attended to the aeroplane. After doing so she started the propeller, and as she walked away from it the machine suddenly moved forward. Pluckily, Miss Spooner jumped and caught hold of the wing, her idea being to clamber into the cockpit and stop the engine. The machine quickly gathered speed, and she was dragged 40 or 50 yards [she later reckoned it was about 30 yards], when to the horror of the crowd the plane turned and buried its nose in the ground, hurling Miss Spooner some distance. She was unconscious. Doctors were sent for and she was taken to hospital. 'We thought she must have been killed,' an eye-witness told our representative." She was taken to Savernake Hospital suffering from a sprained wrist, cuts, and slight concussion. She does seem to have had quite a few run-ins with the local Constabulary; firstly in January 1929 for failing to keep her Alsatian dog under proper control (it had attacked another dog which "had no chance"), then in August 1929 for failing to produce a car driving licence (she said she had forgotten about it and flew to France the following day); then in 1931, she was fined £35 for leaving her motor car unattended and for failing to have lights on it. When she was told that she would be reported, she said: "I am used to it." A police-superintendent said there were no previous convictions recorded against her, as far as Reading was concerned. The Chairman then asked 'And none in the air? She replied 'There are no policemen in the air. That is why I like it.'" I'm certainly sorry I missed her talk, given in April 1928 at Harrods in Brompton Road, on "Flying as a New Delight for Womankind". Later, in the early thirties, she wrote for "Good Housekeeping" on, of course, "Flying for Women", alongside such luminaries as John Galsworthy, Kate O'Brien, and Hugh Walpole.
September 1929 saw her accompanying NFS's chairman Freddie Guest (q.v.) to Nairobi, to inaugurate an air taxi service and give flying lessons. They took 3 aeroplanes with them, and flew them back (via South Africa) in February 1930. She and E C T 'Cecil' Edwards tried to fly a Desoutter to Cape Town and back in December 1930, but this expedition ended up in a forced landing in the sea off southern Italy; Cecil and Winifred had to swim a couple of miles to shore.
She regularly competed in the King's Cup - coming 3rd in 1928 - and was a guest at Amelia Earhart's reception at the Royal Aero Club in May 1932.
She was personal pilot to Leicestershire M.P. Lyndsey Everard from February 1931 - they are seen here with Nigel Norman. And then, suddenly, on 13 January 1933, she was dead - not in an air crash, but as a result of a cold which rapidly worsened into pneumonia. Only few days before, in conversation with a friend, she had mentioned that her mother had died from influenza in 1918. "The deaths of both mother and daughter occurred with the same suddenness." They are buried together in Hinton Parva: see http://www.earlyaviators.com/espoone5.htm
She left £1,357 0s 8d, and her brother, Capt. Frank Vivian Spooner, Indian Army (retd) was appointed administrator. She hadn't got round to writing a will. There is a scholarship in her memory at Sherborne School for Girls. "In the passing of Winifred Spooner the world has lost a great woman... she stood out as a woman of indomitable courage". Winifred owned: a 1926 DH.60 Moth (G-EBOT), a 1928 DH.60G Gipsy Moth (G-AAAL, which she sold to Elise Battye); a 1930 Desoutter IID (G-ABCU - this is the aeroplane she and E.C.T. Edwards ditched in the sea off Naples in December 1930), and later a 1932 Breda 33 (G-ABXK), which was sold in Italy just 3 months before her death. Winifred's brother Tony was chief flying instructor at the Montreal Flying Club in 1931. He was killed in March 1935 in Egypt when piloting a D.H. 84 Dragon, SU-ABI belonging to Misr Airwork, when it was caught up in a sandstorm and both engines failed. |
|
- Details
- Hits: 2855
| Capt Thomas Neville Stack | ||
|
|
RAeC [0312-0087] |
|
|
b. 1 April 1896; universally known as 'Stacko' RFC in WWI, then became a familiar figure in aviation circles during the 1920s - in 1926 he and Bernard Leete made the first flight from England to India in two DH. Moths, one of several record-breaking flights. He and J R Chaplin tried to fly to Australia and back in 1931, but had to turn back at Constantinople, Turkey, with carburettor trouble; later in the year the same pair attempted a flight to India and back, but again turned back with mechanical problems. He was appointed 'Air Superintendent' of Iraq Airwork Ltd in 1933, and flew their first machine (a Spartan Cruiser) there via Cairo in 1933. Shortly afterwards, he flew 2 doctors and a nurse out to India, to perform an urgent operation on a Nepalese princess. Late 1933 found him testing the Airspeed Courier - which is probably where he met Sydney Turner - and was widely expected to fly it in the MacRobertson Race. A month before the race, he broke (his own) London-Copenhagen record in a Miles Hawk, which is perhaps why he was too busy to inspect the Viceroy properly.... He turned up for the MacRobertson Race looking very tired and drawn - Alan Goodfellow described him as looking 'over-trained, physically', and Neville Shute Norway said he was "an exhausted and a worried man". Shortly after the race, he was appointed Air Superintendent and Manager of Hillman's Airways; after that became part of British Airways he spent time in Turkey, advising them on civil aviation. He was killed when run over by a lorry in Karachi, India on 22nd February 1949, aged 52. At first, the Karachi Police said he had committed suicide but, while agreeing that he was 'on the verge of a nervous breakdown', the inquiry decided that the cause of death was actually an aneurism of the aorta, and he would have died anyway. Neville was "always very good company. He was never happier than when singing a song and strumming on his banjo." |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2614
| Flt-Lt Christopher Stainbank Staniland | ||
|
|
|
|
|
A Schneider Trophy pilot, in 1928. Fairey's chief test pilot from 1936; 'His real love is motor racing' (well, thanks very much). bailed out from the same aircraft twice in one day. Killed in WWII: 26 June 1942 in a Fairey Firefly; buried Keddington, Lincs. |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2566
| F/O Joseph 'Mutt' Summers | ||
|
|
|
|
| 'Mutt' Summers, chief test pilot for Vickers and Supermarine. Flew the Spitfire prototype on its first flight.
Called 'Mutt' because he liked to pee on or near his aeroplane before taking off; is that too much detail? Still has the most flying hours of any test pilot in the world. d. 1954. |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2337
| F/O G Thorne | ||
|
|
|
|
| ?? | ||
- Details
- Hits: 2431
| Flt-Lt Charles Frederick Le Poer Trench | ||
|
photo: 1917, when 2nd Lieut in the RFC, aged 22 |
|
|
| An Australian who was a SPAD pilot in WWI; died in Sydney in 1974. | ||
- Details
- Hits: 2258
| Mr Alexander Frew Wallace | ||
|
|
|
|
|
from Kalmalcolm, Scotland |
||
- Details
- Hits: 2283
| Mr Allen Henry Wheeler CBE MA | ||
|
|
|
|
|
b. 27 Sep 1903, Bitterley, Ludlow Ed. Eton, University of Cambridge RAF 1925-55: RAF Officer (Engineering); at Boscombe Down and Farnborough during WWII Trustee, Richard Ormonde Shuttleworth Remembrance Trust, Old Warden, Beds, from 1947 to 1980 4th place in the Kemsley Challenge Trophy, Birmingham, 31 Jul 1949 1 of 3 assessors, BOAC DH106 Comets G-ALYP & G-ALYY Accident Enquiry, Ministry of Transport & Civil Aviation, 19 Oct to 24 Nov 1954 Wrote ' That Nothing Failed Them' (1963), 'Building Aeroplanes for those Magnificent Men' (1965), and 'Flying Between the Wars' (1972) Aviation Consultant and Technical Advisor to the film industry, including 'Those Magnificent Men in their Flying Machines' (1965) and 'The Blue Max' (1966) Member of GAPAN, 22 Sep 1966 President of RAeS Bedford Branch (FRAeS), 1977-78
d 1 Jan 1984 - Whistley Bridge, Berks
Research: thanks to Steve Brew |
||



 1930
1930 Jack', chief test pilot for for Blackburn, later a Wing Commander. Susan Slade's cousin.
Jack', chief test pilot for for Blackburn, later a Wing Commander. Susan Slade's cousin. photo: 1913, when Leading Seaman Ashton, aged 25
photo: 1913, when Leading Seaman Ashton, aged 25 photo: 1929
photo: 1929 photo: 1929, aged 25
photo: 1929, aged 25
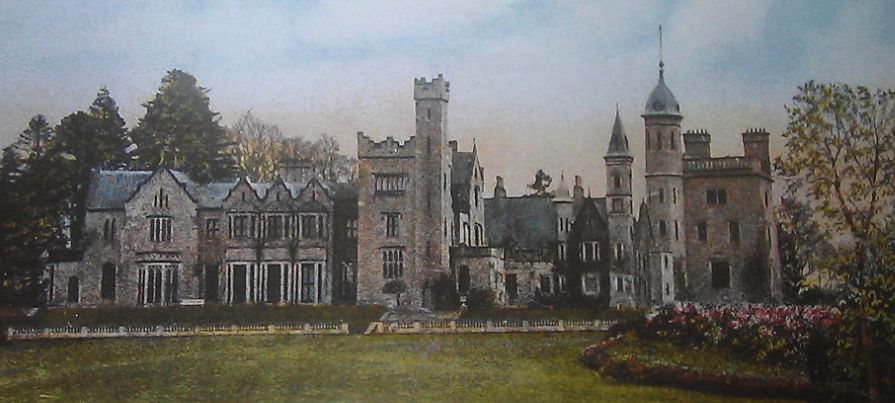 www.monaghan.ie/museum
www.monaghan.ie/museum Throttle Full Open
Throttle Full Open
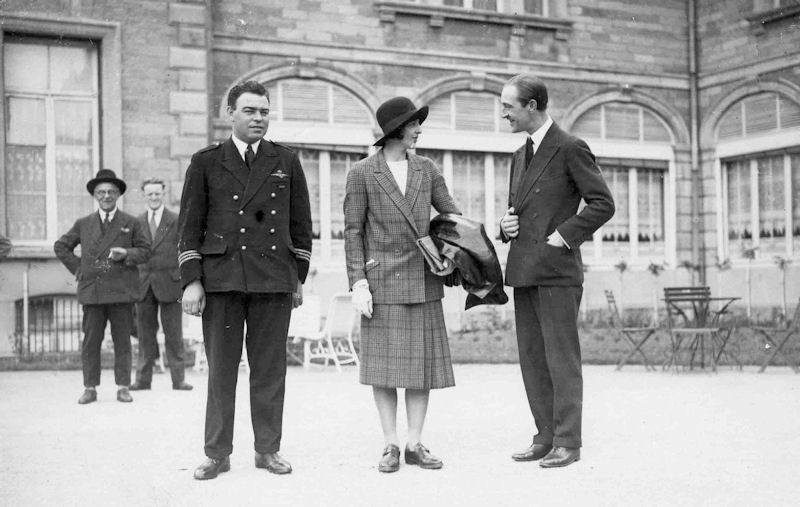
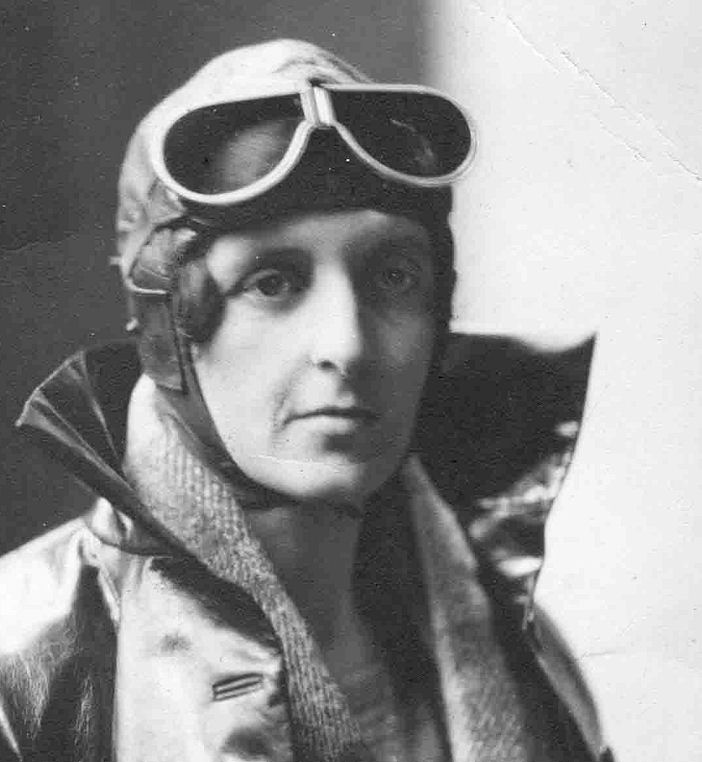




 photo: 1930
photo: 1930 photo: 1930, aged 33
photo: 1930, aged 33

 King's Cup 1933
King's Cup 1933 photo: 1927, aged 35
photo: 1927, aged 35
 1911, aged 29
1911, aged 29  1936, aged 54
1936, aged 54
 1930
1930 1917, when a 2nd Lieut in the RFC, aged 20
1917, when a 2nd Lieut in the RFC, aged 20 1928, aged 31
1928, aged 31 1926, aged 38
1926, aged 38 1927, aged 23
1927, aged 23 1928, aged 29
1928, aged 29


 "To the beloved and wonderful memory of Haliburton Hume Leech".
"To the beloved and wonderful memory of Haliburton Hume Leech".
 1916, when a Lieut, 15th Hussars, aged 27
1916, when a Lieut, 15th Hussars, aged 27 1937, aged 30
1937, aged 30 1916, when a 2nd Lieut in the 2/5th Royal Warwickshire Regiment, aged 25
1916, when a 2nd Lieut in the 2/5th Royal Warwickshire Regiment, aged 25
 1936
1936![Kings Cup 1938 Tommy Rose [0122-0170]](/images/gallery/air%20races/preview/333s333/Kings%20Cup%201938%20Tommy%20Rose%20%5B0122-0170%5D.jpg)





.jpg)




 1934, aged 38
1934, aged 38
 1938
1938 1930, aged 26
1930, aged 26
 1927, when a medical student, aged 28
1927, when a medical student, aged 28 1948, aged 46
1948, aged 46